Blog
When organizations partner with a drug testing laboratory, they’re not just buying test results; they’re buying efficiency, reliability, and options. One of the most important (and often overlooked) differentiators in a lab partner is the ability to test specimens both clinically and forensically. Understanding the difference and the value of having access to both can help organizations streamline operations while still meeting their goals.
When to Choose Forensic Testing
Forensic drug testing is chosen when results must stand up to scrutiny, whether that’s in legal, regulatory, employment, or disciplinary contexts. The defining feature of forensic testing is a documented chain of custody, which tracks the specimen from collection through final result, ensuring it is properly handled, securely stored, and free from tampering at every step. This rigorous process, combined with mandatory confirmation testing and strict documentation standards, makes forensic results defensible and reliable if they are ever questioned. When decisions carry higher risk or long-term consequences, forensic testing provides confidence that the results are not just accurate, but indisputable.
When to Choose Clinical Testing
Clinical drug testing is often the right choice when results are used to support care decisions, program oversight, or internal actions, rather than legal or disciplinary proceedings. Because the results are not intended for litigation, clinical testing offers meaningful operational advantages:
- Simpler collections: No chain of custody documentation or tamper-evident seals are required, which reduces administrative burden.
- Less staff time required: Clinical collections are faster and easier to manage, especially important for organizations with limited headcount.
- Faster path to action: Results can be used immediately for insight, case management, or program decisions involving patients and families.
For many organizations, clinical testing delivers exactly what’s needed: accurate results without unnecessary complexity.
Key Differences Between Clinical and Forensic Collections
While both testing types rely on high-quality laboratory science, the collection and handling requirements differ significantly:
- Chain of custody: Required for forensic testing, not required for clinical testing.
- Specimen security: Forensic collections require tamper-evident seals; clinical collections do not.
- Confirmation testing: Mandatory in forensic testing, optional in clinical testing, depending on the use case.
- Specimen transport: Clinical specimens can travel with a simple manifest, rather than formal custody documentation.
These differences directly impact staffing, workflows, and turnaround times, making the choice of testing type a strategic one.
Why a Dual-Capable Lab Is a Smart Partner
Here’s where flexibility becomes a true value add. A laboratory that supports both clinical and forensic testing gives organizations options and safeguards.
- A forensic specimen can be processed clinically if forensic collection requirements weren’t fully met, ensuring results are still available.
- This flexibility helps prevent missed opportunities, recollections, or delays.
- Organizations can adapt testing approaches as needs evolve, without changing lab partners.
In contrast, a clinical specimen cannot be retroactively converted to forensic testing, making it even more important to work with a lab that can guide the right approach from the start.
At USDTL, whether the specimen is tested forensically or clinically, our laboratory maintains forensic protocols for every specimen from receipt until reporting of results, ensuring the highest standards are kept at all times.
The Bottom Line
For B2B organizations that manage drug testing programs, the ideal laboratory partner offers more than testing; they offer operational efficiency, reduced risk, and flexibility. A lab capable of both clinical and forensic testing helps ensure you get usable results every time, aligned with your purpose, your resources, and your responsibilities.

We’re excited to share that USDTL has partnered with CourtFact to make drug and alcohol testing easier to manage for justice-involved programs and service providers. Through this new integration, CourtFact users can access USDTL’s trusted lab-based and instant testing services directly within the platform they already use to manage cases and compliance.
This partnership streamlines workflows, reduces administrative friction, and helps agencies focus on what matters most—supporting their clients and programs.

We’re starting the year with momentum at USDTL. Planning is underway on a new state-of-the-art laboratory facility in Chicago; an investment in our growth, innovation, and ability to serve our partners well into the future.
At the same time, we’re excited to share that USDTL is now processing clinical specimens alongside our long-standing forensic testing. Backed by decades of toxicology expertise, this marks an important step toward expanding how we support the testing community.
Updated: 1/29/26
Due to current weather conditions in Memphis, we expect courier delays in receiving specimens into the laboratory. A delay in receiving specimens would cause a delay in reporting out results. We will do our best to process specimens as quickly as possible and deliver your reports as soon as we can.
Thank you for understanding. If you are also affected by the weather, please stay safe out there.
More information on FedEx’s website.
Click here to read the full abstract. Click here to learn more about our hair testing.

We are excited to announce the addition of ketamine to our umbilical cord tissue testing menu. These substances can be ordered as a 20-panel and add-on beginning July 28, 2025.
Click here to learn more about our new ketamine test.
For more information on umbilical cord tissue testing click here.

The U.S. Department of Justice and Drug Enforcement Administration release an annual “Drugs of Abuse” packet to be “a reliable resource on the most commonly used and misused drugs in the United States.”
Click here to read the 2024 version!
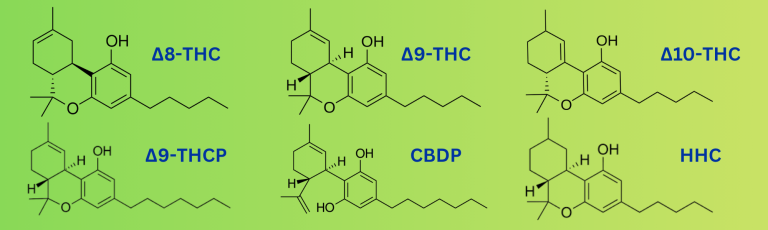
Photo by: USDTL, Delta-8 THCP molecular structure unknown at the time of publication
Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Basics
The term cannabinoid refers to any chemical compound that interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the body’s endocannabinoid system. (2) These compounds are largely derived from Cannabis sativa, a plant that contains approximately 540 known chemical substances. (1) Under the United States’ 2014 and 2018 Farm Bills, plants with very low levels of THC (0.3%) are classified as industrial hemp. (8)
Trending Cannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids are compounds structurally similar to delta-9 THC or CBD but may be synthetically modified or occur in low concentrations naturally, and many have yet to be fully studied. They’re frequently found in vape cartridges, oils, gummies, and other over-the-counter products that can work around federal regulations. (3)
One of the major public health concerns with these types of cannabinoids is the accuracy of product labeling. For example, over-the-counter CBD products may contain significantly more or less CBD than listed. Due to limited regulatory oversight, they may also contain contaminants like THC without the consumer’s knowledge. (1) This both complicates toxicology testing and risks unintentional intoxication, especially in vulnerable populations like children.
Dr. Donna Coy, Ph.D., NRCC-TC, Laboratory Director at USDTL, highlights the main concern for public health:
“Different cannabinoids that circumvent the legal status of marijuana are being seen in the forensic toxicology field. These other cannabinoids have a different structure or are hemp-derived and may be illegal, depending on local legislation. Someone could use these products and have a negative delta-9 THC result.”
Here are some of the trending phytocannabinoids being seen on the market:
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC) is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant in small quantities. However, delta-8 is often synthesized from hemp-derived CBD due to hemp’s low natural abundance. (5)
The FDA has raised alarms about delta-8 THC products because of:
- Inconsistent and dangerous product formulations and labeling;
- Unknown cannabinoid and terpene profiles;
- Variable potency and psychoactive effects;
- Misleading “hemp” branding that implies non-psychoactivity;
- Unregulated and/or unsanitary manufacturing conditions. (5)
From January 2021 to February 2022, US poison control centers received 2,362 exposure cases involving delta-8 THC products. (5)
Delta-9 THC
Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) is the primary psychoactive component in cannabis and binds to the CB1 receptor in the body to produce a range of biological and behavioral responses. (6) This means it is the “typical” cannabis product that most are familiar with.
While delta-9 THC and CBD are the most studied phytocannabinoids, several analogs with slight chemical variations are emerging in consumer products. (7)
Delta-10 THC
Delta-10 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ10-THC) is another THC analog with limited research, but it contains known psychoactive potential. It has been associated with multiple poison control reports. Between 2021 and 2022, 5,022 cases involving delta-8 THC, delta-10 THC were reported to US poison centers. (9)
Delta-9-THCP
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol (Δ9-THCP) is thought to be significantly more potent than delta-9 THC. (2) In one case study, a regular cannabis user experienced psychotic symptoms and was hospitalized after consuming 8 mg of THCP. (2)
THCP does appear naturally in cannabis plants but only in small amounts. As a result, most products containing THCP are synthesized or genetically modified. (3) Despite this, its human effects remain poorly understood, and its availability in the commercial market remains controversial.
A study from Haghdoost, et al. states, “Part of this interest [in THCP] is because of the intoxicating effect of THCP, which allows users to achieve a ‘legal high’ by taking advantage of unintended allowances in the wording of the 2018 Farm Bill.” (3) This loophole is because THCP is under the 0.3% THC in dry weight count by federal law, allowing online markets and head shop owners the ability to sell it freely without fully knowing the effects.
Delta-8 THCP
Much like delta-9 THCP, delta-8 tetrahydrocannabiphorol (Δ8-THCP) is synthetically produced and likely psychoactive, but little research exists on its effects.
CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive, naturally-occurring phytocannabinoid that does not cause a “high.” It is commonly used for a range of wellness claims, though scientific understanding of its full effects is still developing. (8) However, CBD is not entirely risk-free. Unknown side effects, drug interactions, and potential contamination are all concerns consumers should keep in mind. (8)
Moreover, many vendors that sell CBD also market THC-containing products. Without proper labeling, consumers may unknowingly ingest psychoactive substances. (8)
For more on this topic, see our blog post “What We Know About CBD.”
CBDP
Cannabidiphorol (CBDP) is a non-psychoactive analog of CBD, also discovered naturally in small amounts in cannabis plants. Much like THCP, its low natural abundance makes mass production difficult, so it is often made synthetically with genetic modifications to the plants to mimic the effects. (3)
Both THCP and CBDP are available in distillates, vapes, and gummies through online platforms, despite little data on safety or long-term impact. (3)
HHC
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a hydrogenated form of THC with trace natural occurrence, typically produced semi-synthetically. It is considered mildly psychoactive and has been marketed widely as a “legal high.” (4)
A 2023 review noted that while HHC products are readily available, there is concern over their potential for misuse or dependency, even though no intoxication cases had been formally reported by that time. The concern comes from its structural similarities to delta-9-THC and “CB1-mediated tetrad effects in mice.” (4) The same study noted concern that HHC is available to purchase on the internet as a “legal” replacement to THC. (4)
Why Test for Them?
Standard drug testing focuses on delta-9 THC, missing many analogs and synthetic cannabinoids that can still impair users and may be misused. With the rise of synthetic and genetically-modified cannabinoids in products marketed as “hemp” or “legal,” toxicology must evolve.
Our extended cannabinoid panels in ChildGuard® can be used for accurate detection in cases involving suspected cannabinoid exposure in vulnerable populations.
References:
- https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11791752/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11277192/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10616920/
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/5-things-know-about-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-delta-8-thc
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2731700/
- https://nij.ojp.gov/library/publications/cross-reactivity-cannabinoid-analogs-delta-8-thc-delta-10-thc-and-cbd-their
- https://www.cdc.gov/cannabis/about/about-cbd.html
- https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2024.2340115
- Forensic vs. Clinical Drug Testing: Why Flexibility Matters for Your Organization
- USDTL’s Integration and Partnership With CourtFact
- New Year, New Capabilities: Offering Forensic & Clinical Testing Options
- Weather Delay
- The Detection of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, Delta-10-tetrahydrocannabinol, and Cannabidiol in Hair Specimens
- Umbilical Cord Tissue Testing for Ketamine
- Drugs of Abuse: A DEA Resource Guide (2024)
- Beyond THC and CBD: Understanding New Cannabinoids
- February 2026 (1)
- January 2026 (3)
- October 2025 (1)
- July 2025 (3)
- May 2025 (2)
- April 2025 (2)




