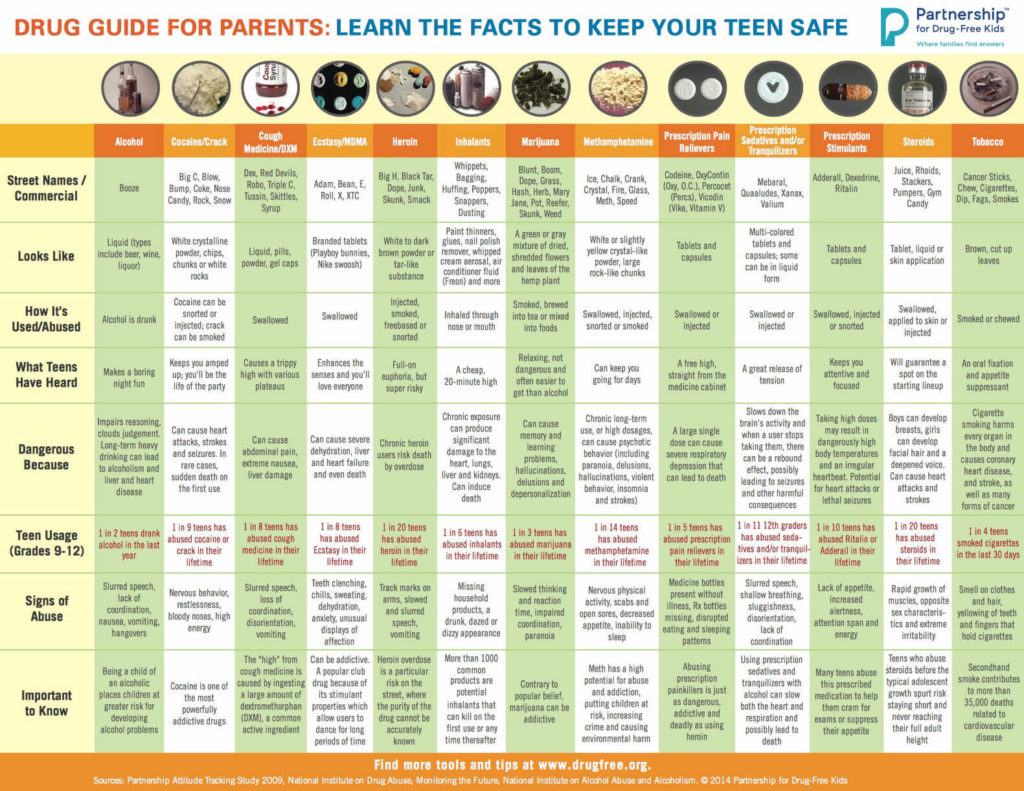
Drug Guide for Parents: Learn the Facts to Keep Your Teen Safe
Showing: drug exposure
To view the larger image, please click here.
What you need to know about meconium collection.
by Michelle Lach, MSIMC
Meconium is the first stool of a newborn infant. It is produced in utero and consists of materials such as epithelial cells, bile, mucous, and more. In most newborns, meconium is generally passed in the first day or so of life, has no odor, and appears as a very dark, tar-like substance. This helps distinguish meconium from the next phase of passage called transitional stool.
Transitional stool will start to have an odor and present with a more brown, green, or yellow color as the newborn starts digesting milk. When drug testing the meconium of a newborn, it is important to note this difference since only meconium is created during gestation and transitional stool is created after birth. Collection of any stool other than meconium for drug testing purposes may result in a rejected specimen.
Unlike umbilical cord tissue, drugs are not distributed uniformly throughout the meconium specimen (see Figure 1). Because of this, the collection of the entire mass of meconium is highly encouraged to assure that there will be enough specimen to test, and that the maximum window of drug detection is achieved. It can take multiple passages of meconium before the newborn begins the transitional stool phase.
We require a minimum of 3 grams of meconium to be able to properly run our tests, so collecting the entire passage of meconium from newborns that have been exposed to substances of abuse is highly critical since they tend to have lower birth weights and create less specimen in the first place. If there is not enough specimen to run the test, the results are reported out as QNS. Quantity Not Sufficient (QNS) is a result of not having a sufficient quantity (volume) of specimen to test for the panels ordered.
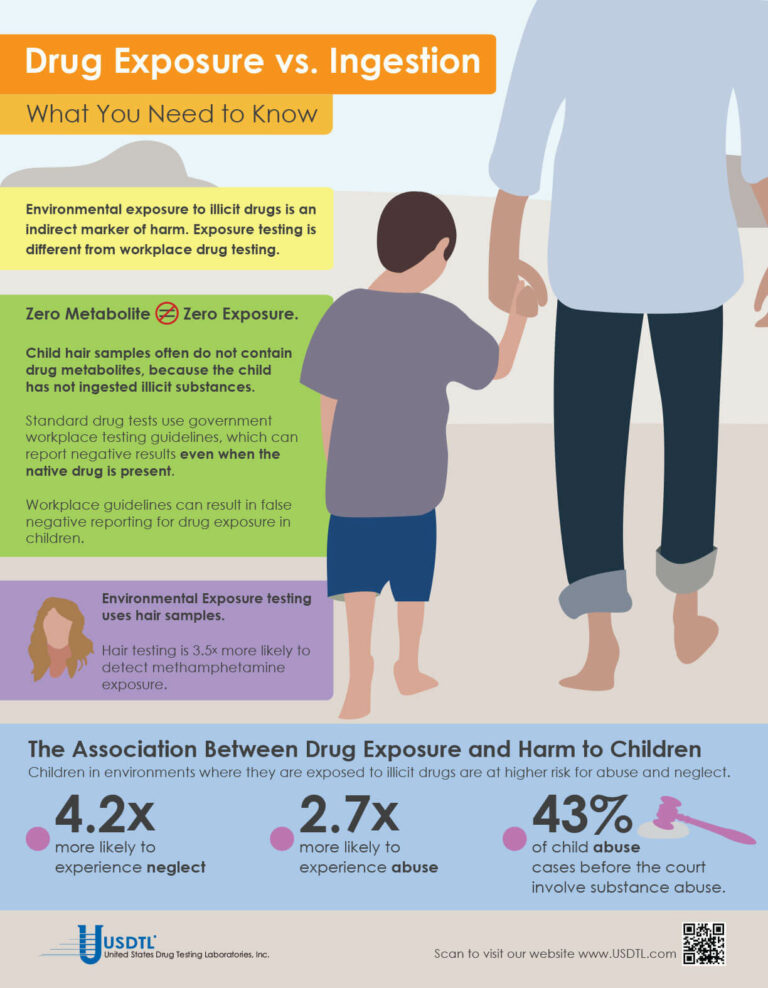
What You Need To Know: Testing for Drug Exposure vs. Ingestion
Testing for environmental exposure to illicit drugs is a powerful tool for protecting the welfare of children. Exposure testing is different from typical drug testing, and when properly done, has the potential to reduce the risk of harm to children.
No Metabolite Does NOT Mean No Exposure
Testing labs often apply government workplace testing guidelines to child exposure testing samples. Under workplace guidelines, negative results are reported when drug metabolites are absent in the testing sample, even if the native drug is present.
Child hair and nail samples for exposure testing often do not contain drug metabolites because the child has not ingested illicit substances. Adhering to workplace guidelines can result in false negative reporting for drug exposure, especially when children are involved.
Environmental Exposure
Environmental Exposure testing is most effective in alternative sample types, such as hair and fingernails. For example, hair testing is 3.5x more likely to detect methamphetamine exposure than urine testing. Typical drug testing samples are washed to remove drug biomarkers resulting from exposure. Environmental exposure testing eliminates this step.
References:
- Kelleher, K., Chaffin, M., Hollenberg, J., & Fischer, E. (1994). Alcohol and drug disorders among physically abusive and neglectful parents in a community-based sample. American Journal of Public Health, 84(10), 1586-1590.
- Murphy, J. M., Jellinek, M., Quinn, D., Smith, G., Poitrast, F. G., & Goshko, M. (1991). Substance abuse and serious child mistreatment: Prevalence, risk, and outcome in a court sample. Child abuse & neglect, 15(3), 197-211.
– Click here to download the pdf.
When a child is exposed to illegal substance abuse they often also face other coexisting obstacles to a normal life – neglect, abuse, violence, and other vulnerabilities. Substance abuse is a disease, one that often prevents adults from doing what is in a child’s best interests. Our environmental exposure test for children can help.
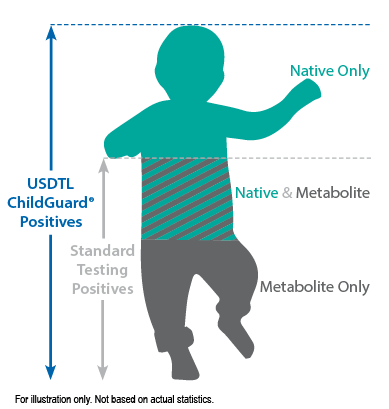
Our hair environmental exposure test is the only drug test designed to detect passive exposure to drugs and detect both native drugs and drug metabolites in the hair specimen. Drug metabolites are produced in the body only if drugs have been ingested. Children in drug exposed environments are most often not drug users themselves, so drug metabolites are typically absent in child specimens. However, the hair, like a sponge, can absorb non-metabolized drug (native drug) if it is exposed through things such as touching or being in contact with drugs or drug users.
Standard hair tests with other labs will only report a positive exposure result if drug metabolites are detected, even when the native drug is in the child’s hair specimen. Our hair environmental exposure test reports a positive result if either native drugs or drug metabolites are detected.
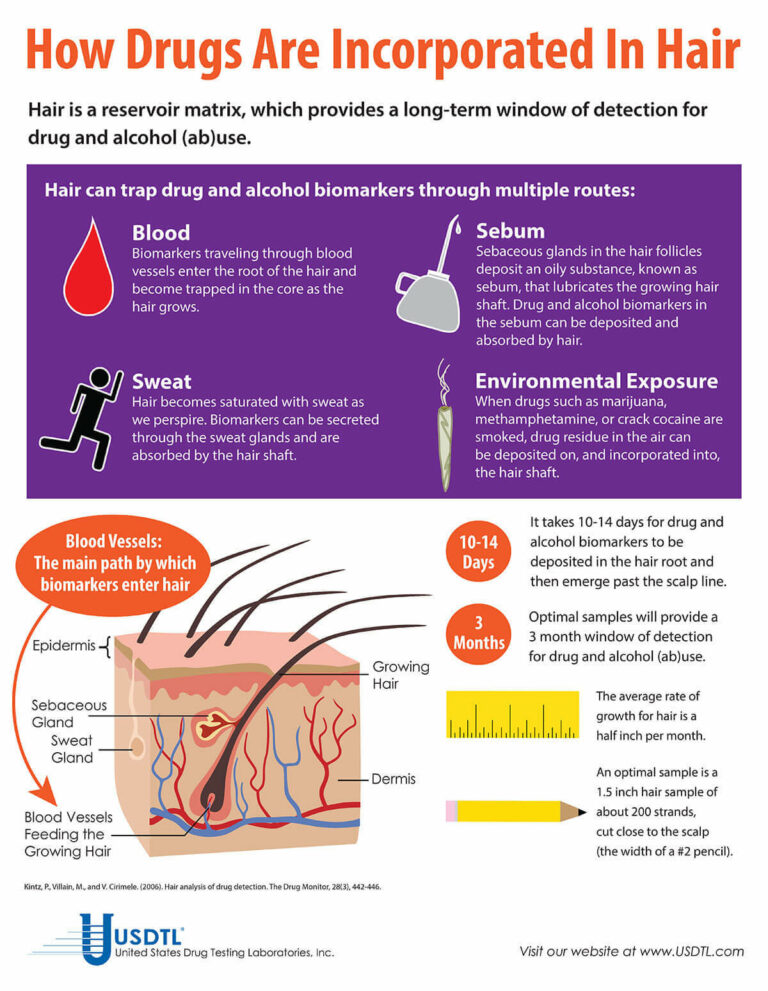
A hair exposure test can provide evidence of drugs in a child’s environment for the past 3 months. A positive test result suggests that the child has experienced one or more of the following: passive inhalation of drug smoke, contact with drug smoke, contact with sweat or sebum (skin oil) of a drug user, contact with the actual drug, or accidental or intentional ingestion of illegal drugs.
ChildGuard®is the only child hair test designed to detect exposure to native drugs and drug metabolites.
- The Detection of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, Delta-10-tetrahydrocannabinol, and Cannabidiol in Hair Specimens
- Umbilical Cord Tissue Testing for Ketamine
- Drugs of Abuse: A DEA Resource Guide (2024)
- Beyond THC and CBD: Understanding New Cannabinoids
- New Xylazine, Psilocin, Gabapentin, Dextromethorphan, and Extended Cannabinoids Testing at USDTL
- Psilocin: The Magic Behind the Mushroom
- Fetal Fentanyl Syndrome: Why Detecting Newborn Fentanyl Exposure Matters Now More Than Ever
- DMT: An Overview
- October 2025 (1)
- July 2025 (3)
- May 2025 (2)
- April 2025 (2)
- March 2025 (2)
- February 2025 (1)